مواد متداول استفادهشده و ویژگیهای اتصالدهندههای کواکسیال RF چیست؟
مواد تشکیلدهنده کانکتورهای هممحور RF میتوانند بر خواص مکانیکی، الکتریکی و محیطی آنها تأثیر بگذارند. بنابراین، در فرآیند اولیه طراحی کانکتور، انتخاب مواد اولیه تعیینکننده عملکرد کلی دستگاه سیستم خواهد بود. به عنوان یک طراح کانکتورهای هممحور RF، باید الزامات مختلفی از جمله خواص مواد، نیازهای اتصال و هزینه را در نظر گرفت.
مواد اولیه برای انتقال فرکانس رادیویی (RF) بسیار حیاتی هستند، زیرا به عنوان پایهای برای مدارهای بدون وقفه عمل کرده و از تداخل در مدار جلوگیری میکنند. در این فصل، ما از ساختار اتصالات هممحور فرکانس رادیویی شروع خواهیم کرد و به طور خاص مواد رایج و ویژگیهای مؤلفههای تشکیلدهنده این اتصالات را معرفی خواهیم کرد.
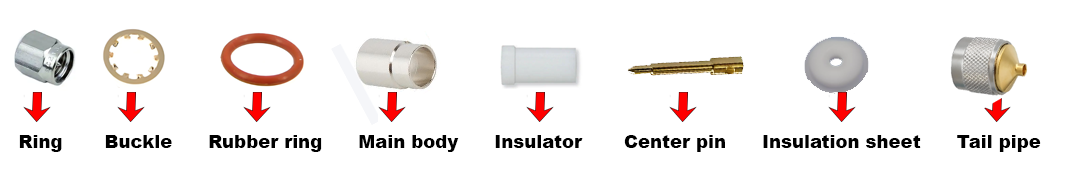
ساختار coaxial اجزای اتصال
مواد فلزی رایج
در میان اجزای مختلف اتصال هممحور فرکانس رادیویی، غلاف پیچ، بدنه اصلی، پین مرکزی، کاپ سOLDER و لوله دمی همگی محصولات فلزی هستند. برنج بریلیمی، برنج قلع فسفرو، برنج و فولاد ضدزنگ از مواد فلزی رایج در اتصالات هممحور فرکانس رادیویی هستند که هر کدام مزایای خاص خود را دارند.
B بریلیم مس
(1) برنج بریلیمی دارای خواص خوب الکتریکی و انتقال حرارت، مقاومت در برابر خستگی و مقاومت قوی در برابر خوردگی (به جز در مقابل آمونیاک، اسیدهای قوی و بازها) است؛
(2) عملکرد خوب انتقال حرارت و کشسانی از ذوب شدن آن در محیطهای دمای بالا جلوگیری میکند و سایر خواص نیز توسط دماهای بالا آسیب نمیبینند.
بریلیم برنز معمولاً برای سوراخها یا سوکتهای تماس (جایی که اتصالات الکتریکی ایجاد میشوند)، پینهای کشسان و هادیهای خارجی در رابطها استفاده میشود.

قلع فوسفور برنز
(1) بافت این ماده آلیاژی نسبتاً نرم است و میتواند از طریق فرآیند سرد (فشردهسازی، خم کردن) تحت تنش قرار بگیرد؛
(2) به دلیل نرمی آن، برنز قلع-فسفر جایگزینی برای انواع دیگر آلیاژهای مس شده است. زمانی که بودجه تولید اجازه نمیدهد یا عملکرد الکتریکی لزومی به استفاده از بِریلیم برنز ندارد، میتوان از برنز قلع-فسفر به عنوان جایگزین استفاده کرد.
برنز قلع-فسفر را میتوان برای سوکتهای بزرگتر، تماسهای کشسان یا هادیهای خارجی استفاده کرد.

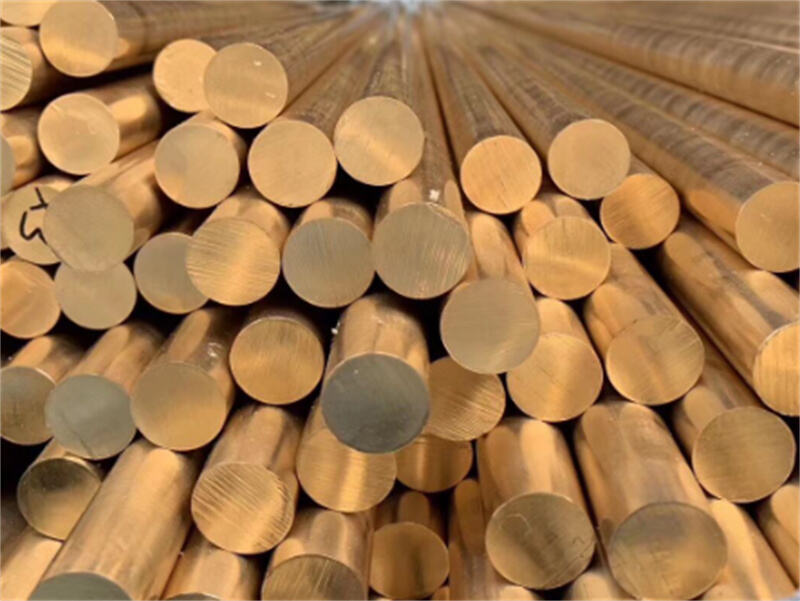
B برنج
(1) برنج دارای بافتی نرم است و به راحتی ماشینکاری میشود و به همین دلیل به «برنج قابل برش آسان» معروف است. در مقایسه با برنز بریلیومی، برنج تماس حرارتی خوبی دارد و هدایت حرارتی بالاتری دارد؛
(2) این ماده مقاومت مناسبی در برابر آلودگی و خوردگی ناشی از صنعت، دریا، کشاورزی، جو و انواع روغنها دارد. معمولاً برای بهبود مقاومت در برابر خوردگی و استحکام آن، سطح آن را با طلا، نقره، آلیاژهای سهگانه یا نیکل الکترولس میپوشانند.
برنج معمولاً در تولید بدنه کانکتورها، پوستهها، هادیهای خارجی و پینها استفاده میشود.

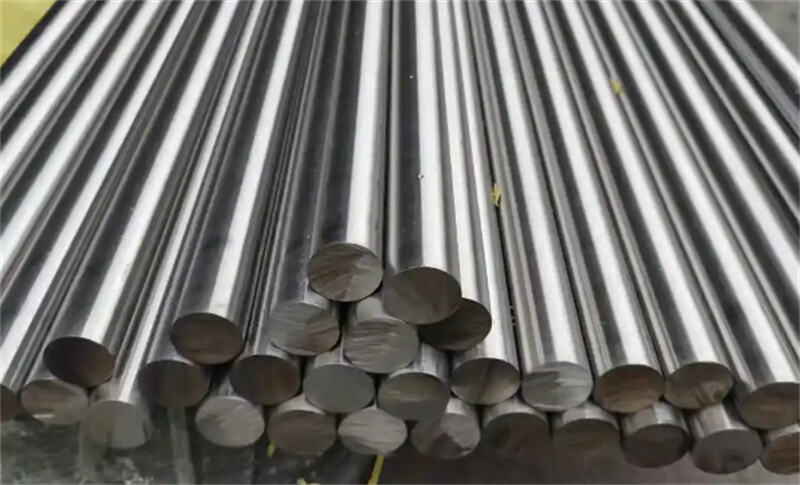
اس استیل بی ند
(1) فولاد ضدزنگ در مناطقی که نیاز به سختی بالای ماده در صنعت کانکتور وجود دارد، مانند هادیهای خارجی، کاربرد دارد؛
(2) پایداری بالا، نقطه ذوب بالا و مقاومت عالی در برابر خوردگی. فولاد ضدزنگ برای ساخت برخی قطعات پوسته کانکتور، مانند غلاف خارجی، استفاده میشود.
فولاد ضدزنگ معمولاً به عنوان ماده پایه، ماده پوسته یا ماده هادی خارجی به کار میرود.

آمپر آلیاژ آلومینیوم
(1) آلومینیوم معمولاً به صورت آلیاژ استفاده میشود که رایجترین آن آلیاژ "آنتیکوردال" است.
(2)آلیاژ آلومینیوم فرآوری آسانی دارد، خواص الکتریکی و انتقال حرارتی خوبی دارد و دارای ویژگیهای خودحفاظتی (مقاومت در برابر اکسیداسیون)، بافت سبک و عملکرد مناسب در پردازش مکانیکی است. گاهی به عنوان جایگزین برخی فلزات (برنج، فولاد ضدزنگ) استفاده میشود.
از آلیاژ آلومینیوم میتوان برای لولههای محافظ و قطعات ساختاری متصلکنندهها استفاده کرد.

مقایسه ویژگیهای مواد رایج
|
F ویژگی |
B بریلیوم B برنز |
فلز P فسفر B برنز |
B برنج |
اس استنلس اس فولاد |
آمپر آلومینیوم آمپر لوی |
|
C تماس ر وجود |
+ |
+ |
+ |
- |
+ |
|
W سایش مقاوم |
-- |
0 |
- |
+ |
- |
|
C خوردگی مقاوم |
0 |
0 |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
P قیمت |
- |
+ |
- |
++ |
- |
توجه: مقادیر نسبی از ++ (خیلی خوب/قیمت پایین)، + (خوب/قیمت پایین)، 0 (متوسط)، - (ضعیف) تا -- (خیلی ضعیف/قیمت بالا) متغیر است. *مقاومت تماسی باید حدالامکان کم باشد (++ بسیار پایین، عالی)
من عایق
همچنین به عنوان پایه یا صفحه نصب شناخته میشود. این قطعه، جزء اصلی کل اتصالدهنده است و ابعاد خارجی و موقعیتگذاری هر بخش از اتصالدهنده را تعیین میکند. مواد آن عموماً پلاستیکی هستند.
- عایقبندی الکتریکی بین ترمینالها؛
- موقعیت هندسی انتهای ثابت، عامل تسهیل در ورود و پایداری ابعادی است؛
- فراهم کردن حفاظت مکانیکی و تکیهگاه برای ترمینالها؛
- جداسازی ترمینالها از محیط کاربرد، به منظور کاهش حساسیت به خوردگی
اس درزگیر ر کردن
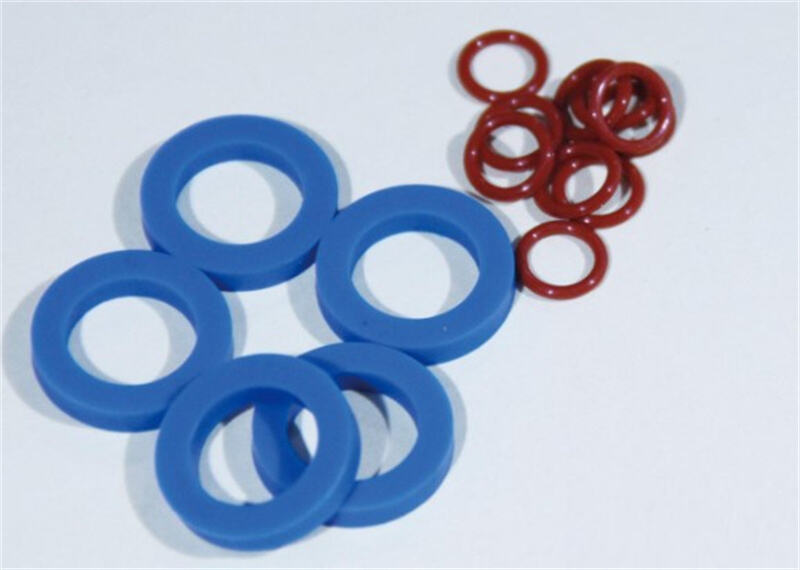

مواد متداول پلاستیکی و لاستیکی
مواد پلاستیکی و لاستیکی، علاوه بر مواد فلزی، دو ماده اساسی مهم دیگر در ساخت اتصالدهندههای هممحور RF هستند. عایقها و حلقههای درزگیر از مواد پلاستیکی و لاستیکی ساخته میشوند.
کف
درپوش خارجی اتصالدهنده است
وظایف شامل تقویت ساختار، تعریف رابط اتصالات نری و ماده، موقعیتیابی برد مدار چاپی (PCB) اتصال و بهاشتراکگذاری محافظت مکانیکی خارجی است.
از نظر الکتریکی، این قطعه دارای عملکردهایی مانند محافظت در برابر تداخل الکترومغناطیسی (EMI) و ارتینگ الکترواستاتیک (ESD) است.

تماس
این جزء اصلی یک اتصالدهنده است که وظیفه اتصال الکتریکی را بر عهده دارد و به آن «سر تماس» یا «ترمینال تماس» نیز گفته میشود. معمولاً یک زوج تماس از یک سر نر و یک سر ماده تشکیل شده و اتصال الکتریکی از طریق فرو رفتن و تماس بین سر نر و ماده انجام میشود.
- ترمینالهای نر معمولاً از جنس برنج ساخته میشوند که دارای هدایت الکتریکی خوبی است اما انعطافپذیری کمی دارد؛ شکل قطعه تماس نر عموماً استوانهای (سیمپیچ گرد)، مربع استوانهای (سیمپیچ مربع) یا صفحه تخت (برشه) است.
- ترمینالهای زن معمولاً از جنس فسفر-مس ساخته میشوند که هرچند هدایت الکتریکی ضعیفی دارند، اما انعطافپذیری خوبی دارند. شکل قطعه تماس زن شامل انواع استوانهای (با شیار تقسیمشده و دهانه مخروطی)، نوع شاخهدار (تونیگ فورک)، نوع جعبهای (سوکت مربعی) و غیره است.

لوازم جانبی
ملحقات به دو دسته ملحقات ساختاری و ملحقات نصب تقسیم میشوند.
- اتصالات ساختاری: حلقههای نگهدارنده، پینهای مکانیاب، پینهای راهنما، حلقههای اتصال، کلمپ کابل، حلقههای آببند، واشرها و غیره
- ملحقات نصب: پیچها، مهرهها، حلقههای فنری، واشرها و غیره
اخبار داغ
-
کانکتور RF کواکسیال چیست؟ ویژگی ها و کاربردهای آن چیست؟
2025-07-01
-
کانکتور BNC
2024-07-22
-
کانکتور sma
2024-07-19
-
تفاوت بین وصلکهای BNC و SMA
2024-07-03
-
چه مزایایی برای کابلهای同軸 ضد اغتشاش وجود دارد
2023-12-18
-
راهنمای کامل به دانش پایهای وصلههای کابلهای同軸
2023-12-18
-
چرا توانایی ضد اغتشاش کابلهای کلی same-axis اینقدر قوی است
2023-12-18

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 UR
UR
 HA
HA
 JW
JW
 LA
LA
 MY
MY
 KK
KK
 TG
TG
 UZ
UZ
 AM
AM
 PS
PS

